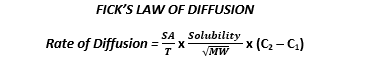K1iv / 25A05 / 15A03: Structure + Function of BBB
25A05: Exam Report
With respect to the blood brain barrier (BBB), outline the following:
- the structure (15% of marks).
- its function (25% of marks).
- the mechanisms by which substances, including drugs move across the BBB and explain how this is determined or regulated (45% of marks).
- the regions that lie outside the BBB and their purpose (15% of marks).
24% of candidates passed this question.
The most effective way to approach this question was to structure information into the headings provided and consider the mark allocation to determine the level of detail for each section.
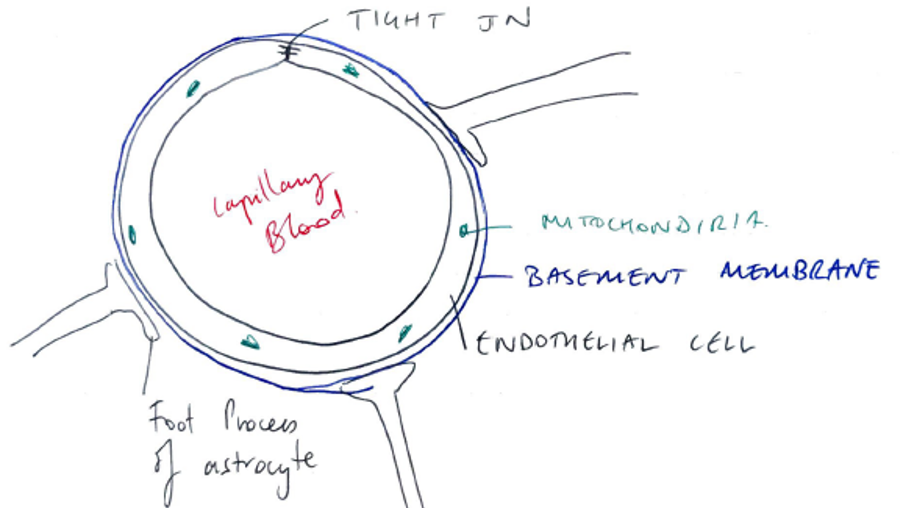
High scoring answers described the unique physical and biochemical features that make up the blood barrier (such as the capillary endothelial cells with tight junctions and numerous mitochondria), and relate these to its barrier and regulation functions.
Part (c) required detailed information about the factors affecting permeability across the blood brain barrier and includes transporters and efflux pumps.
Answers that provided examples of specific substances and how they move across the blood brain barrier scored best.
When responding to the areas outside the blood brain barrier, answers that included not just the area but the rationale similarly scored higher.
15A03: Exam Report
Describe the structure and function of the blood brain barrier.
33% of candidates passed this question.
There was general lack of understanding of the conceptual framework of the blood brain barrier (BBB) and its function. To attain a pass, candidates were required to describe the concept of BBB as a physical and a transport barrier, describe the role of tight junctions and glial cells and identify important barrier functions with some examples of things commonly transported across or excluded.
K1iv / 25A05 / 15A03: Describe the structure and function of the BBB
- BBB = highly regulated interface which separates the CNS from the blood
Function of the BBB
- CNS homeostasis → provides a stable environment for neurons
- Protect brain from toxins
- Tight control of electrolytes
- Protects brain from transient ∆BGL
- Prevents release of central NT into systemic circulation
Endothelial Cells
- No fenestrations
- Have TIGHT JUNCTIONS
- Prevents passage of molecules from blood → brain
- Multiple mitochondria → large amounts of Active Transport
Astrocytes
- Contain many enzymes which metabolise substances before they can reach BBB
Drugs Metabolised by BBB
- MAO → breaks down dopamine & NA
- ∴we can’t give dopamine to Rx PD
- We must give L-DOPA which is then converted to dopamine
- Cholinesterases → metabolise ester Las
Substance Regulation
(Small + lipid soluble)
- CO2
- O2
- EtOH
- Nicotine
- H2O
↓
PASS
Cannot Pass
- Electrolytes
- Proteins
- Ab’s
- Hydrophyllic
BBB Transport
- Diffusion: CO2, O2, EtOH, H2O
- Facilitated: amino acids, glucose (GLUT – 1)
- Receptor mediated endocytosis (Insulin)
- Paracellular transfer
Circumventricular Organs
- Area where BBB is absent
↓
- Have neuroendocrine role ∴need access to systemic circulation
- Vomiting centre (area postrema)
- Pineal gland (secretes melatonin)
- Neurohypophysis of the PPG (releases oxytocin + ADH)
Disruption to BBB
- Inflammation
- Oedema
- HTN (stretching & weakening tight junctions)
- Epilepsy (↑BP → weakens TIGHT JUNTIONS → restored 1hr post seizure)
Drugs to Penetrate CNS
- Solubility = required to be lipid soluble. CNS covered by 2 layers of membrane → BBB & PM of neurons
- Size = smaller = better. Must be <400Da
- Ionisation = penetration is in the UNIONISED FORM
∴ weak acids penetrate CSF better
- CNS Metabolism = drugs metabolised in CNS will create a gradient for diffusion
- Inflammation = loss of BBB integrity will ↑SA available & ↑rate of drug diffusion e. antibiotics for meningitis
- Author: Krisoula Zahariou