G2iii / 24B13 / 18A12: Ventricular diastole
24B13: Exam Report
(a) Define ventricular diastole, including its usual duration (15% of marks). (b) Describe the cardiovascular events that occur during this period (85% of marks). (ionic and cellular events not required)
38% of candidates passed this question.
A thorough response to this question provided an accurate definition of ventricular diastole providing detail about duration (either duration at a certain heart rate or the usual ratio with changes due to tachycardia).
The second part was best structured by dividing the events into cardiac mechanical and electrical events and circulatory changes.
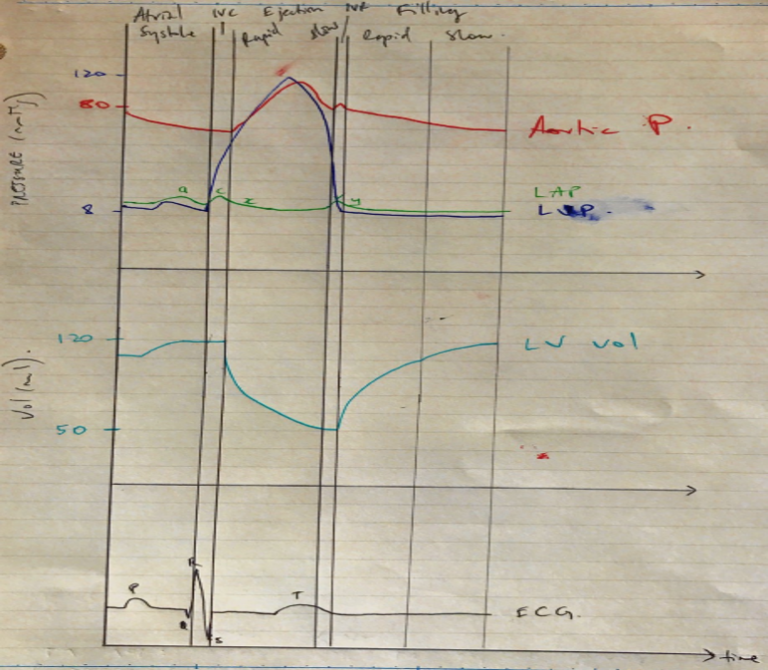
Mechanical events included a description of isovolumetric relaxation, early filling, atrial ejection and isovolumetric contraction, with an explanation of what marks the beginning and end of each of these phases as well as what happens to pressures within the cardiac chambers.
Electrical events included the correlation of diastole with ventricular repolarisation and refractory periods as well as the corresponding ECG waves.
Finally, an overview of the changes that occur in the coronary, pulmonary and systemic circulations during diastole was expected.
18A12: Exam Report
Briefly describe the cardiac events that occur during ventricular diastole.
29% of candidates passed this question.
Many answers lacked structure and contained insufficient information. Better answers defined diastole and described the mechanical events in the 4 phases of diastole. A common error was the ECG events in diastole. The electrical events and coronary blood flow should have been mentioned.
G2iii / 24B13 / 18A12: Describe the cardiovascular events that occur during ventricular diastole
Definition
Begins with closure of aortic (or pulmonary) valve and ends with the closing of mitral (or tricuspid) valve. For HR 60bpm approv 0.5sec duration
Diastole = the period of the cardiac cycle where the ventricles relax & fill
- Lusitropy = the ability of cardiac myocytes to relax
- Events of diastole divided into:
- Ionic ∆
- ECG ∆
- Mechanical ∆
NOTE: Most cardiac work occurs during diastole
1) Ionic
- Cytosolic [Ca2+] regulates active events of myocytes
- ↓[Ca2+] causes Ca2+ to dissociate from TnC & inhibits cross-bridging
- ↓Ca2+ is facilitated by:
- SERCA pump → pumps Ca2+ back into SR
- Sarcolemma Ca2+-ATPase → moves Ca2+ extracellularly
- Facilitates myocyte relaxation (lusitropy)
2) ECG
- Isovolumetric relaxation: ventricular repol. Is being completed → end of T-wave on ECG
- Rapid filling: no electrical activity by cardiac cells ∴isoeletric line on ECG
- Slow filling: depol. spreads from SA Node across atria → P wave on ECG
- Atrial contraction: atrial depol. complete → end of P wave. Depol spreads from atria → AV Node = PR segment on ECG
3) Mechanical Events
- There are 4 phases of ventricular diastole
- Isovolumetric relaxation
- Rapid filling
- Reduced filling
- Atrial systole
4. Isovolumetric relaxation
- All ventricles relax
- Ventricular pressure falls
- Outflow tract P > ventricular P → blood flow reverses → aortic + pulmonary valves shut
- Valves shut = S2 = commencement of DIASTOLE
- All valves are shut → ventricular volumes remain constant
- Volume in ventricle KA ESV ~50mL
5. Rapid filling
- Atrial P > ventricular P → AV valves open
- Ventricle fills with blood → fast because atria were so full prior to AV valve opening
- Filling is passive
- Once ventricles are fully relaxed → their pressure begins to rise as they fill
6. Reduced filling
- Passive ventricular filling nears completion
- Ventricle is filling with blood & expanding, but becoming less compliant
- As the ventricular P increases, the rate of blood flow from atria → ventricle will fall
7. Atrial systole
- Atria contract → drives more blood into ventricle
- Atrial pressure falls → reserving pressure gradient across AV valves → AV valves shut
- At the end of this phase, ventricles are filled to their ECV ~120mL with P 3mmHg
- Author: Krisoula Zahariou