2019 - Multiple Choice Questions
The end-systolic pressure volume relationship (ESPVR) of the cardiac pressure-volume diagram is a measure of:
- Afterload
- Contractility
- Diastolic function
- Preload
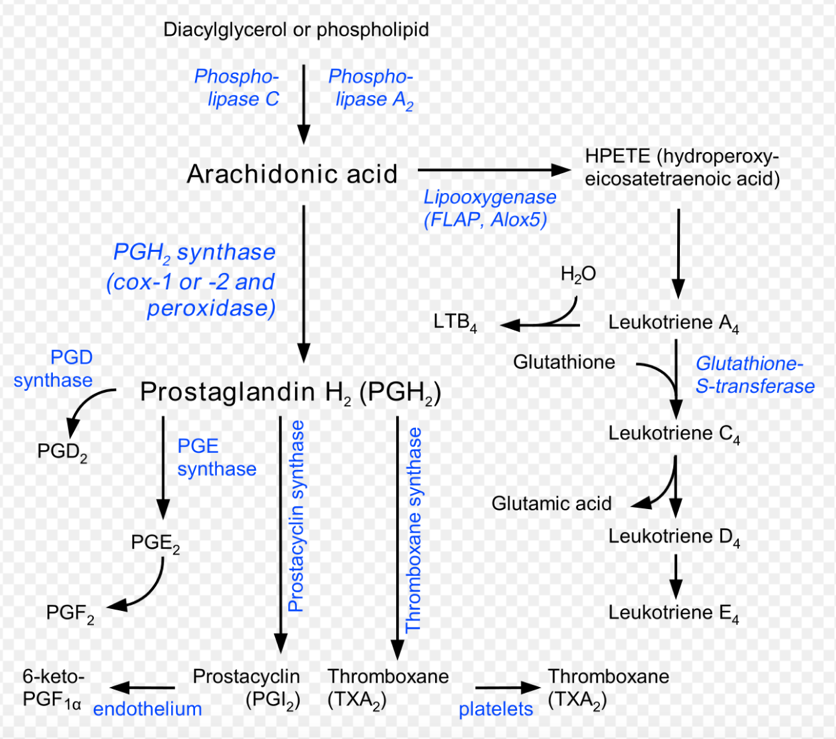
Acetylsalicylic acid inhibits the cyclo-oxygenase enzyme resulting in:
- Bronchodilation
- Increased leukotriene synthesis
- Increased prostaglandin synthesis
- Reversible platelet inhibition
- COX inhibitition
- Increases lipooxygenase pathway
Oxytocin has the following effects in-vivo:
- Gastric mucosal protection
- Hyponatraemia
- Systemic hypertension
- Tocolysis
Oxytocin is structurally similar to anti-diuretic hormone (ADH, vasopressin) and both are released from the posterior pituitary. Onset is ~1 min when given IV, and t1/2 is ~5 min.
- The most common side effect is hypotension
- Prolonged infusions can result in water retention and hyponatremia due to cross reactivity with the vasopressin receptor, giving rise to water intoxication.
Metformin exerts its hypoglycaemic effect by:
- Increasing insulin secretion by pancreatic beta cells
- Inhibiting alpha-glucosidase enzymes
- Inhibiting gluconeogenesis and delaying glucose absorption from the gastrointestinal tract
- Stimulating pancreatic alpha cells to release insulin
Which of the following neuromuscular junction blocking drugs can induce a Phase II Block?
- Cisatracurium
- Rocuronium
- Suxamethonium
- Vecuronium
Mechanism of Phase II Block. With increasing doses of succinylcholine (i.e., a large single dose, repeated doses, or a continuous infusion), a phase II block may occur. Continuous activation of acetylcholine receptors leads to ongoing shifts of sodium into the cell and potassium out of the cell.
Which of the following methods is used to measure plasma volume?
- Chromium labelled red blood cells
- Deuterium oxide – TBW
- Inulin – ECF
- Protein bound dyes (e.g. Evans blue)
Ketamine has the following pharmacodynamic effect:
- Antisialagogue
- Bronchoconstriction
- Decreased intracranial pressure
- Direct myocardial depression
What is the mechanism of action of carbapenem antibiotics?
- Inhibition of bacterial cell wall synthesis
- Inhibition of bacterial DNA synthesis
- Inhibition of bacterial ribosomes
- Inhibition of folate metabolism
Which of the following exhibits the HIGHEST potency at the a1 adrenoreceptor?
- Clonidine a2/a1 = 200:1
- Dopamine
- Metaraminol
- Noradrenaline
Drugs that are eliminated by a first-order process exhibit the following kinetics:
- A constant proportion of drug is eliminated per unit time
- A constant quantity of drug is eliminated per unit time
- The clearance is directly related to the time constant (Tau)
- The elimination rate constant is directly related to the half-life
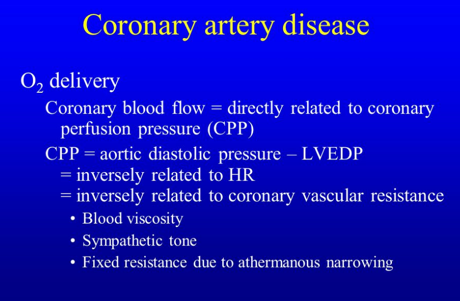
Coronary perfusion of the left ventricle is dependent on:
- Diastolic pressure minus left ventricular end-diastolic pressure
- Diastolic pressure time index
- Mean arterial pressure minus left ventricular end-systolic pressure
- Systolic pressure time index
Which of the following local anaesthetics is the MOST cardiotoxic?
- Bupivacaine
- Lignocaine
- Prilocaine
- Ropivacaine
katzung, pp 426, brunton, pp 377)most local anesthetics can block na+ channels in cardiac muscle and thus they can depressautomaticity and conduction. at very high doses they can also depress contractility, likely byblocking ca++ channels. bupivacaine is more cardiotoxic than most other local anesthetics,apparently because the drug dissociates much more slowly than other local anesthetics duringdiastole, so a significant fraction of na+ channels at physiological heart rates remains blockedwith bupivacaine at the end of the diastole. bupivacaine induced cardiac toxicity is very difficult totreat and is enhanced by coexisting acidosis and hypoxemia)
Regarding acyclovir, which of the following is MOST true?
- It binds to cell membrane receptors leading to the induction of resistance of that cell to viral infection
- It inhibits the release of viral particles from infected cells
- It inhibits viral reverse transcriptase
- It requires viral thymidine kinase for activation
Effects of insulin include the stimulation of:
- Beta oxidation of fatty acids
- Glycogenolysis
- Hormone sensitive lipase
- Lipoprotein lipase
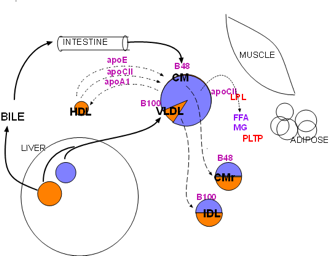
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL, red) is synthesized primarily by skeletal muscle and adipose tissue. It is secreted into the interstitial fluid then diffuses to nearby capillaries. It becomes attached to large, branched proteins (haparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs) bound to the inner capillary surface (not shown). Its function is to hydrolyze triglycerides (lavender) from lipoproteins into free fatty acids (FFA) and monoglycerides

The structure of aldosterone is best described as a:
- Cholesterol derivative
- Single chain polypeptide
- Two chain polypeptide
- Tyrosine derivative
Noradrenaline:
- Has a half-life of 20 minutes
- Increases blood flow to the pregnant uterus
- Is a derivative of tyrosine
- Must be protected from light
Central chemoreceptors:
- Are in the brainstem, in close proximity to the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves
- Are located outside of the blood brain barrier
- Are sensitive to pO2
- Respond to a change in pCO2 over several hours
Intracellular calcium ion concentration in a resting cell is most likely in the range of:
- 0.0001 to 0.001 mmol/L
- 0.001 to 0.01 mmol/L
- 0.01 to 0.1 mmol/L
- 0.1 to 1.0 mmol/L
Which of the following adverse effects is associated with propofol?
- Adrenocortical suppression
- Bradycardia and metabolic acidosis
- Exacerbation of acute intermittent porphyria
- Raised intracranial pressure
- Bradycardia and metabolic acidosis
- Resets baroreceptor reflex
- Metabolic acidosis –PPF infusion syndrome
Erythrocytes:
- Are approximately 20 pm in diameter and 7 pm in thickness
- Are flexible and easily deformed
- Provide about 30% of the buffering power of whole blood
- Survive in the circulation for an average of 160 days